GN Vitamin B12 Complex 120 vegan capsules of 500mcg
GN Vitamin B12 Complex 120 vegan capsules of 500mcg
Low stock: 1 left
Couldn't load pickup availability
GN Vitamin B12 Complex 120 capsules of 500mcg each
Buy Vitamin B12 Complex in the Supplement Support online shop!
Product Highlights
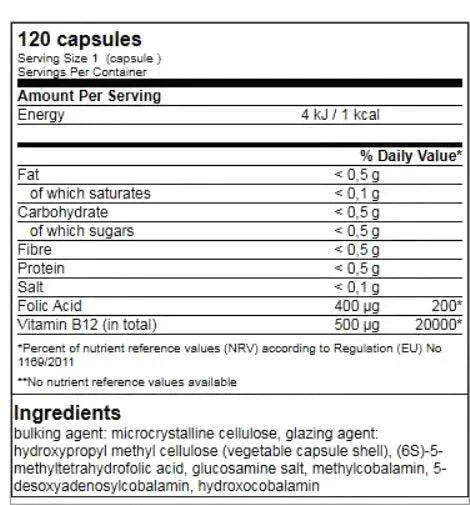
- 120 capsules = 120 daily servings
- High-dose vitamin B12
- can prevent a deficiency
- high bioavailability
- With 3 different forms of vitamin B12
- Is essential for optimal functioning of the nervous system
- It is essential for blood formation
- Vegan
- You can find even more vitamins HERE!!!
Vitamin B12 Complex
The vitamin complex that can protect you from a B12 deficiency with all its negative effects on health and athletic performance, and also takes into account the important interplay of vitamin B12 and folate.
Product Highlights:
To meet the increased B12 requirements of athletes, vegans and other people with increased vitamin B12 needs.
Can counteract a widespread deficiency of vitamin B12 and folate
Helps maintain optimal energy and fat metabolism for maximum training energy.
It is essential for blood formation and therefore also essential for the optimal supply of nutrients to your hard-working muscles.
It is essential for optimal functioning of the nervous system and therefore also for optimal muscle function.
Contains biologically active folate instead of biologically inactive folic acid, which must first be converted into folate in the body.
With 3 different forms of vitamin B12 for optimal effectiveness
Contains 500 mcg of vitamin B12, which is 166 times the daily requirement.
Due to the very close interaction between vitamin B12 and folate, unlike most vitamin B12 complex products, it contains both of these essential vitamins to ensure the best possible effect.
Suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
Vitamin B12 Complex
Vitamin B12 is an essential vitamin that the human body cannot produce itself and therefore must be obtained through food or in the form of supplements.
Strictly speaking, vitamin B12 is not a vitamin, but a group of compounds known as cobalamins, which are enzymatically converted in the body into the active form of vitamin B12 called cyanocobalamin.
In our Vitamin B12 Complex, we use three different cobalamins to ensure optimal absorption and utilization.
Vitamin B12 is needed for a whole range of vital bodily processes, including cell division, energy metabolism, the function of the nervous system, DNA synthesis, blood formation, the synthesis of numerous important hormones and neurotransmitters, fat metabolism, and the breakdown of homocysteine, which is associated with arteriosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases. As you can see, vitamin B12 is also essential for a number of processes that are important for athletes and bodybuilders (without cell division there is no muscle growth; with impaired blood formation, the supply of oxygen and nutrients to your muscles is compromised; with impaired energy metabolism, you will lack energy for training, etc.).
What are the consequences of a vitamin B12 deficiency?
Although it is often claimed that a vitamin B12 deficiency is unlikely with a typical Western diet, some studies show the exact opposite (1). While a “true” deficiency appears to be present in only about 10% of the population, almost 40% have very low vitamin B12 levels in the lower normal range, which is far from optimal.
Early symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can be quite nonspecific and may include lethargy, fatigue, reduced physical performance, sleep problems, difficulty concentrating, and declining memory (2). In advanced stages, a vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to anemia, damage to the central nervous system, neuropathy (sensory disturbances), and dementia. The insidious nature of a vitamin B12 deficiency lies in the fact that it sometimes only becomes noticeable after years of insufficient vitamin B12 intake, because the body can store vitamin B12 in large quantities in the liver, and serious consequences only become apparent once these stores are depleted.
Which groups of people have an increased need for vitamin B12?
Athletes who need more vitamin B12 due to intense physical exertion
Older people, as vitamin B12 absorption decreases with age.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women, whose vitamin B12 requirements are increased and for whom a deficiency can negatively affect the development of the child.
Smokers and people who consume a lot of alcohol, as both impair the absorption and utilization of vitamin B12.
People with impaired intestinal health, as the absorption of vitamin B12 through the intestine may be severely restricted in these cases.
Why vegans need vitamin B12 supplementation
Since vitamin B12 is found almost exclusively in foods of animal origin, it is practically impossible for vegans to meet their needs through diet alone (3), making supplementation necessary. While it is often claimed that certain algae, such as spirulina, contain vitamin B12, this is primarily pseudovitamin B12, which is not bioavailable to humans (4). Fermented soy products, sauerkraut, and other fermented foods do contain vitamin B12, but the amounts are so small that meeting the daily requirement is not possible. A particularly insidious aspect of this scenario is that a vitamin B12 deficiency often only becomes apparent after years and is therefore frequently not associated with the switch to a vegan diet.
Why vitamin B12 and folate should be used in combination
Vitamin B12 and folate are closely intertwined in human metabolism. Both are required for the breakdown of harmful homocysteine, which is associated with arteriosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Since vitamin B12 is responsible for converting folic acid—the inactive form of folate—back into active folate, a vitamin B12 deficiency can lead to a functional folate deficiency even with adequate folate intake (5, 6). Conversely, a folate deficiency prevents vitamin B12 from fulfilling some of its functions. In other words, these two vitamins are highly interdependent.
This problem is further exacerbated by the fact that approximately 25% of the population suffers from a genetic mutation known as the MTHFR mutation (10), which impairs the interaction of folate and vitamin B12 in the breakdown of harmful homocysteine (11) and increases the need for both vitamins.
Folate
Folate is a B vitamin that, apart from the aforementioned breakdown of homocysteine, is needed for cell division, blood formation, protein and fat metabolism, and DNA synthesis, among other things. Since the inactive folic acid often used in supplements must first be enzymatically converted into active folate in the body (7), we use folate directly in our vitamin B12 to avoid this unnecessary step.
A folate deficiency can lead to respiratory problems, inflammation of the mucous membranes, diarrhea, loss of appetite, weight loss, depression, anemia, and cardiovascular disease. Studies indicate that approximately 80% of the population does not consume sufficient amounts of folate (8, 9), which is likely related to the fact that folate and folic acid are destroyed by 40 to 70% during cooking.
Recommended intake
Take 1 capsule daily, swallowed whole with plenty of water.
Note regarding this product
Due to new EU regulations (Health Claims Regulation), we are unfortunately no longer able to provide you with detailed information about products and their ingredients. However, our team is available by email or telephone to the extent permitted by law.
Share

FAQs
Got a question? We are here to answer


