GN Laboratories Iron 120 Vegan Capsules
GN Laboratories Iron 120 Vegan Capsules
Low stock: 1 left
Couldn't load pickup availability
GN Iron 120 Vegan Capsules
Buy minerals like iron in the Supplement Support online shop!
Product Highlights
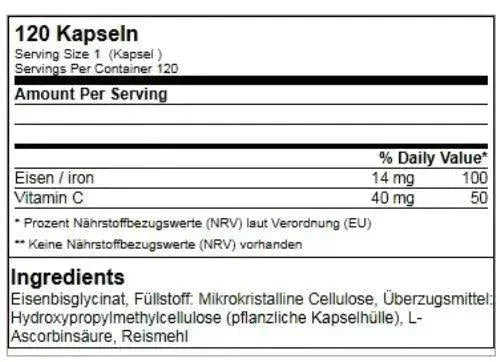
- 120 Veggie Caps per pack
- 14mg iron per capsule
- Reduces tiredness and fatigue
- It can help to address iron deficiency in people with increased iron requirements.
- Can prevent so-called athlete's anemia
- Contributes to blood formation and optimal oxygen transport
- Required for optimal immune system function
- Contains highly bioavailable iron biscyglycinate
- With vitamin C for better absorption
- Suitable for vegetarians and vegans
- You can find even more minerals HERE!!!
:-)
Take 1 capsule daily with sufficient water, without chewing.
What does the body need iron for?
It is an essential trace element that the body cannot produce itself and therefore must be supplied through food or in the form of dietary supplements.
Iron performs a number of vital functions in the human body. It is an essential component of hemoglobin, the red blood pigment, which is necessary for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the various tissues of the body and for removing carbon dioxide from the body's cells. Without sufficient iron, blood cell production and therefore the body's oxygen supply are impaired.
Furthermore, iron is a component of a variety of different enzymes that play an important role in the immune system, among other things, in fighting infections and pathogens.
Athletes will find it interesting that iron is needed to store oxygen in the muscles, where it is required for energy metabolism, which provides the energy needed for intense muscle contractions. However, this is not the only role iron plays in energy metabolism. Iron is also required for the transfer of electrons during energy metabolism, a fundamental physical process without which the entire energy metabolism would not function.
In addition, iron contributes to a reduction in tiredness and fatigue, as well as to normal cognitive function (1).
What are the consequences of an iron deficiency?
Studies have found that in Germany, approximately 14% of all men and 58% of all women do not consume enough iron (2). Additionally, iron requirements can be increased due to various factors, including blood loss (menstruation in women, blood donation, injuries), gastrointestinal diseases that reduce iron absorption, increased needs during pregnancy, and increased iron loss in athletes who train intensively.
Early symptoms of iron deficiency include chronic fatigue, weakness, decreased athletic performance, headaches, forgetfulness, gastrointestinal problems, hair loss, dull hair, brittle nails, dizziness, pale skin and mucous membranes, and increased susceptibility to infections due to a weakened immune system. In advanced stages of iron deficiency, anemia and impaired body temperature regulation can occur.
What makes iron deficiency so insidious is that it doesn't become noticeable immediately, but only when the body's iron stores are depleted. Once such a condition has developed, it can take a considerable amount of time, even with the help of iron supplements, to restore normal iron levels in the body.
Which groups of people have an increased need for iron?
Athletes who train intensively have a significantly increased iron requirement due to iron loss through sweat and other factors. The resulting iron deficiency is colloquially known as "athlete's anemia," but it should not be confused with true anemia. According to studies, 85% of all endurance athletes have hemoglobin and hematocrit levels, which are markers for iron status, only in the lower end of the normal range, which is far from optimal.
Premenopausal women: Due to blood loss during menstruation, the female body loses iron, which must be replenished through food or supplements.
Pregnant women have twice the iron requirement compared to non-pregnant women, which is difficult to meet through diet alone.
Vegans and vegetarians: Because the iron contained in plant-based foods is so-called non-heme iron, which is absorbed by the body 4 to 5 times less efficiently than the heme iron contained in meat, and because plant-based iron sources often contain phytates and other compounds that inhibit iron absorption, iron deficiency is widespread among vegetarians and especially vegans.
How can iron absorption be improved?
Many foods contain substances that form poorly soluble compounds with iron or block iron absorption for other reasons. These include phytates, polyphenols, phosphates, and oxalic acid found in many plant-based foods such as spinach, soybeans, and cocoa; calcium in dairy products; and tannins in tea and coffee. Certain dietary fibers, such as bran, can also inhibit iron absorption.
To ensure optimal iron absorption, GN Iron should be taken on an empty stomach about one hour before a meal.
At GN Iron, we use highly bioavailable iron bisglycinate and have also added vitamin C, which improves iron absorption in the body.
negation
- COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) No 432/2012 of 16 May 2012 establishing a list of permitted health claims made on foods other than claims relating to the reduction of disease risk and to children’s development and health
- www.fet-eb.eu, 2016 Information about iron (Fe), DACH reference values for nutrient supply (1st edition 2015)
Due to new EU regulations (Health Claims Regulation), we are unfortunately no longer able to provide you with detailed information about products and their ingredients. Our team is available to you by email or telephone, to the extent legally permissible.
Share

FAQs
Got a question? We are here to answer


